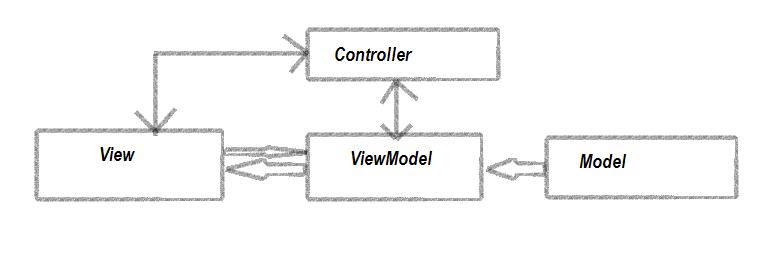
MVC is an architectural pattern that separates your application into three major parts for better maintenance and processing.
ASP.NET MVC just follows the principles of the MVC architectural pattern, where the Model represents business entities and business logic, the View represents the UI(HTML), and the Controller handles the HTTP requests and coordinates with the Model and View to process the request.
It should be very clear that in MVC, the view is only for UI, which is pure HTML. Any other logic in view is actually a violation of MVC principles and considered bad programming practice.
Now, see the following images that will clear your every doubt about why putting any logic in view is a bad idea.
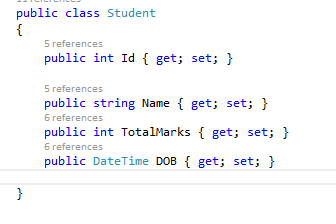
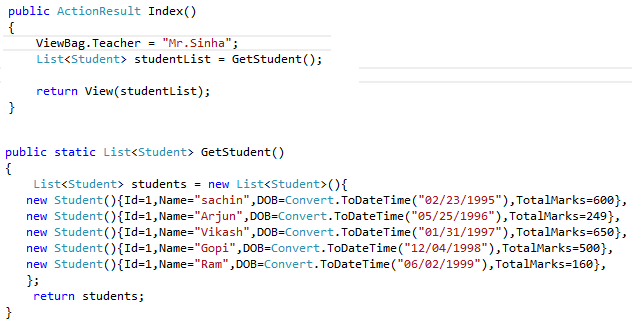
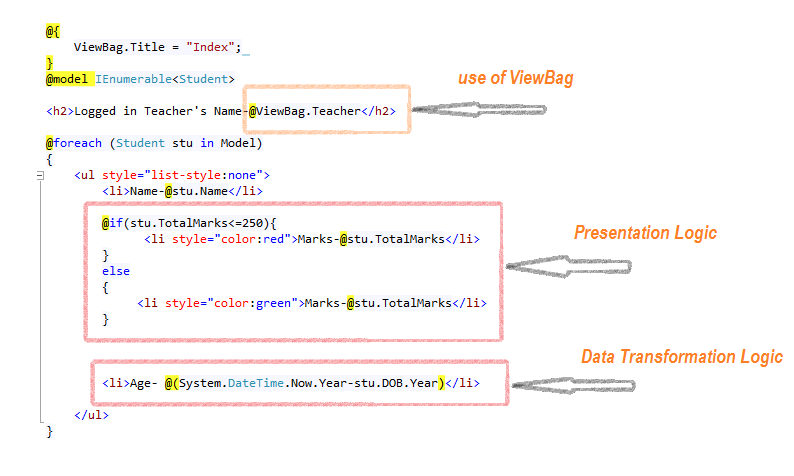
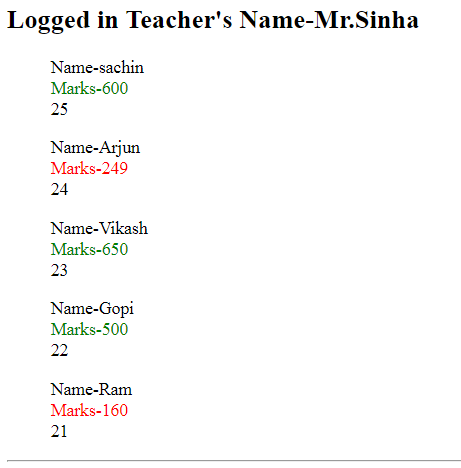
The final output is good and expected, yet it has the following problems:
Why putting Presentation Logic in View is Bad?
Here, if a student's total marks are less than or equal to 250, his marks are shown in red, which symbolizes that the student has failed in the examination, and if his marks are greater than 250, the mark is shown in green, meaning he has cleared the examination.
Now, wait for a moment and think, if tomorrow the criteria for passing the examination change from 250, then we will have to change the UI also, but in reality, a UI should only change when any HTML-related modification is needed .
Why Putting Data Transformation Logic in View is Bad?
Here, I am converting the Student's Date of Birth into age by calculating the difference from the present date. What if, tomorrow, the requirement changes and age needs to be calculated differently, such as instead of the present date, the age should be calculated from a specific date? Again, we will have to change the UI, which is obviously not good.
Why ViewBag is Bad/How to Create a Strongly Typed View based on two model classes?
ViewBag does boxing and unboxing, accepts Key as a string, and does not support IntelliSense, which is bad for performance and can be error-prone. That is why the strongly typed view is always recommended. However, a view can only use one model at a time, so using the Teacher Model class and the Student model class collectively becomes impossible.
All the above problems can be solved by creating another layer called the View Model. As the name says, a view model is specific to a view and not to the business entities.
- Any data transformation logic will be handled by the view model.
- Any presentation logic will be handled by the view model.
- A view model can contain any number of properties or can be created with two or more model classes.
Let's replace the Student model used in the above example with StudentTeacherVM and see how it solves the problems:
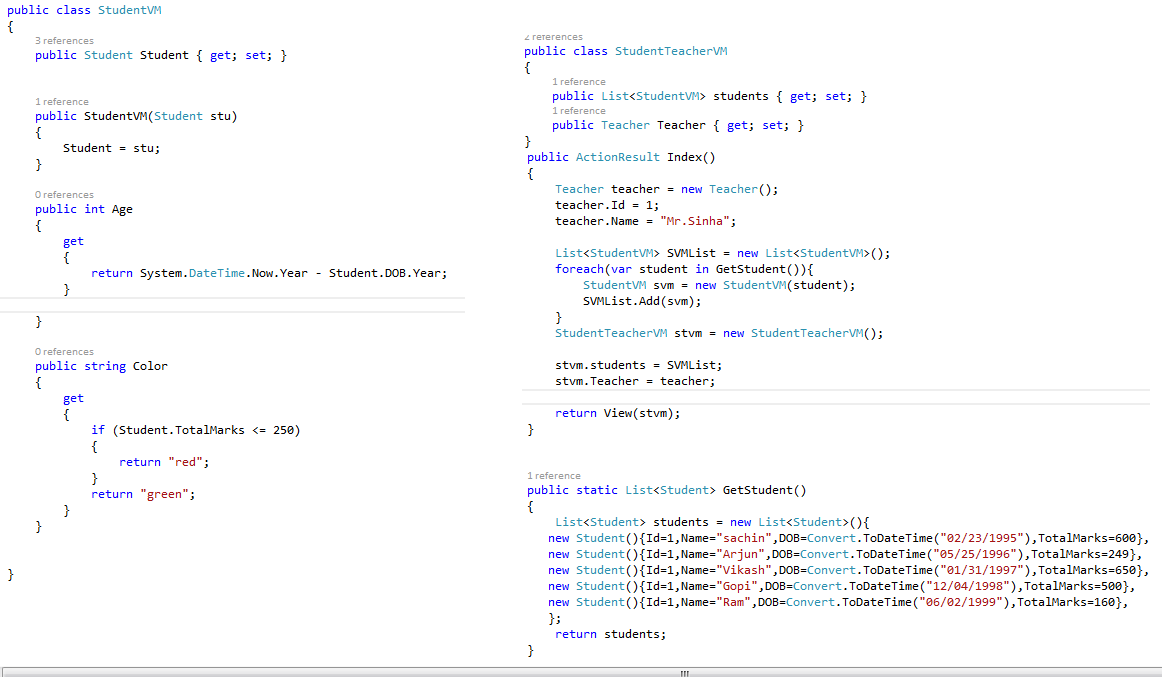
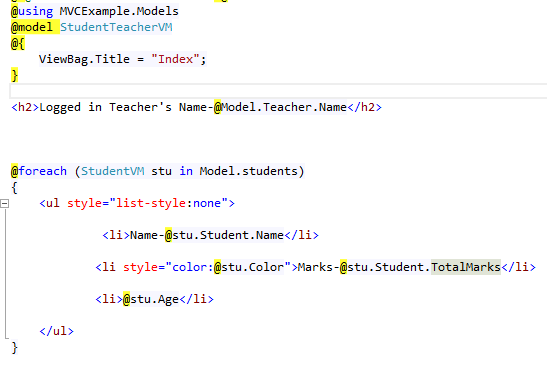

As you can see, the final result is the same, and all the problems have been solved. This is the power of the view model.
Finally, any professional MVC project has the following structure: