Areas in MVC are used for modular development. Now, it becomes important to know what exactly modular development is and what its advantages are.
Breaking a large project into smaller modules is known as modular development and it has the following advantages:
- Faster and parallel development.
- Easier to understand, design, and test than the larger project.
- Ease of debugging and modification, meaning errors can easily be detected and modified.
If we are working on a large project that deals with many functionalities and we have not followed the modular approach, then even for a small modification, we will have to search the whole project, which will take a lot of our time. Similarly, the addition of new functionality will lead to searching the entire project to find the correct place to add it.
On the other hand, if our project is divided into different modules, there will be no need to search the whole project, and we can directly add or modify functionality in the corresponding module.
Areas in MVC serve the same purpose and encourage us to follow a modular approach for application development, improving readability, maintainability, and parallel development.
Suppose you have a large project and you have successfully divided it into different modules like below:
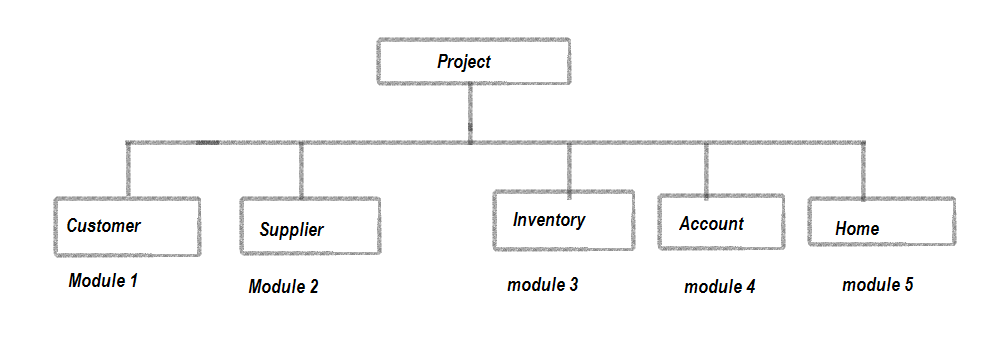
In MVC, each of your modules will be represented by a separate area, as shown below:
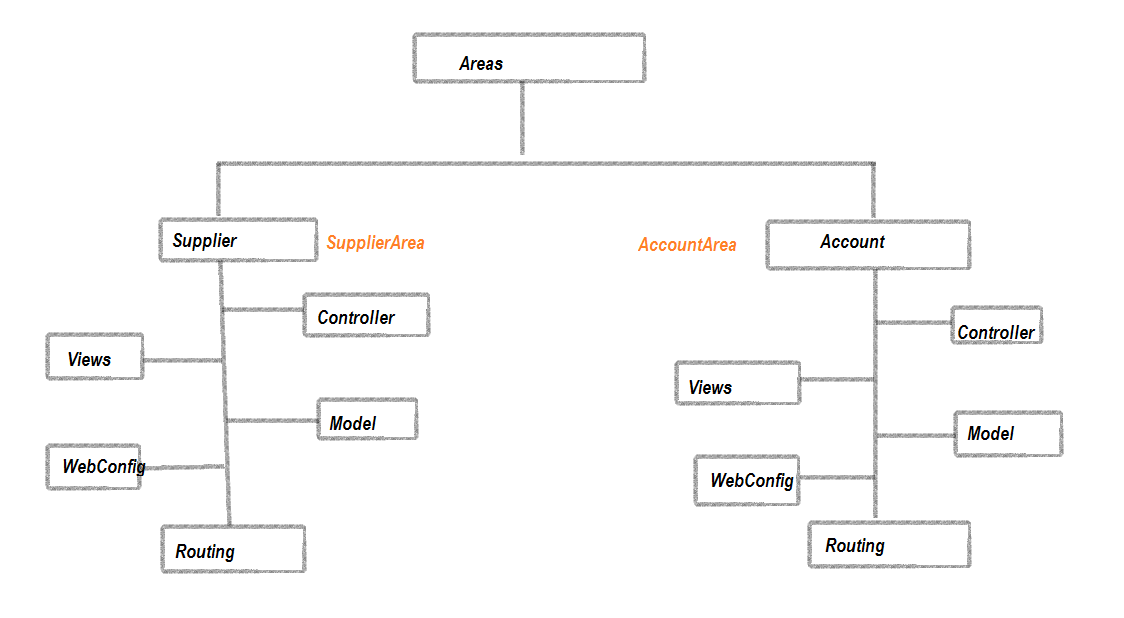
From the above figure, it is very clear that after implementing the Area, each of your modules starts representing an individual Area having its own Controllers, Views, Models, WebConfig, and Routing sections.
So, you do not need to worry about the whole project, and you can easily concentrate on one module at a time. In contrast, other developers can work on other modules without disturbing you in parallel.
Implementing an Area in MVC is very simple and requires adding an area in the project folder as explained below:
Right-click on the project folder, add Area, and give it an appropriate module name, and press Add. That's it.
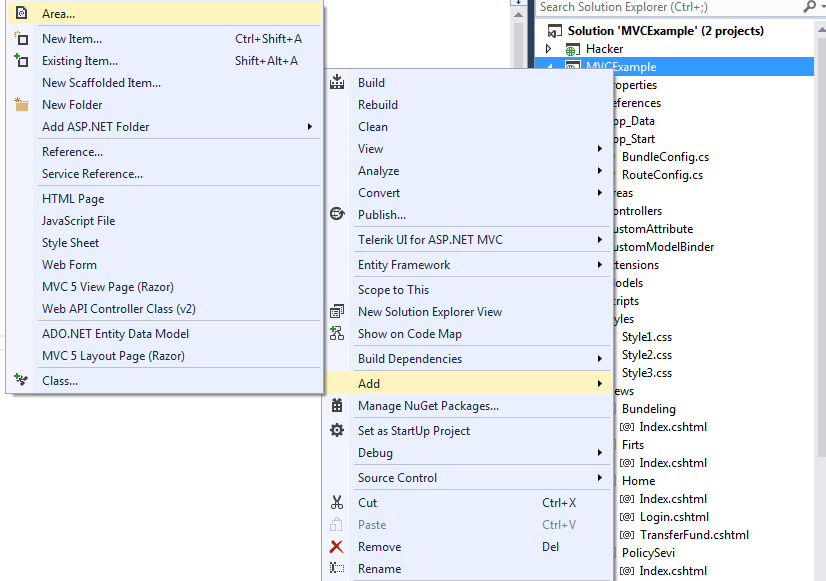
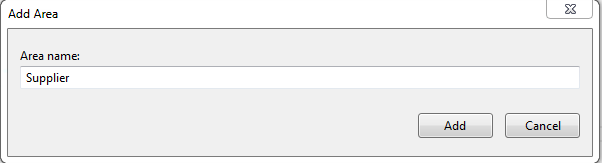
Now, let's check the folder structure of a particular Area created by Visual Studio, under the Areas folder.
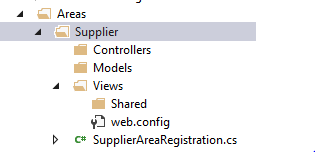
As you can notice, the folder structure of an Area is very much similar to the folder structure of an MVC template. The only difference is that instead of global routing for the whole project, the Area contains its own routing section. The AreaRegistration.cs class contains a RegisterArea method that allows us to define custom routes.
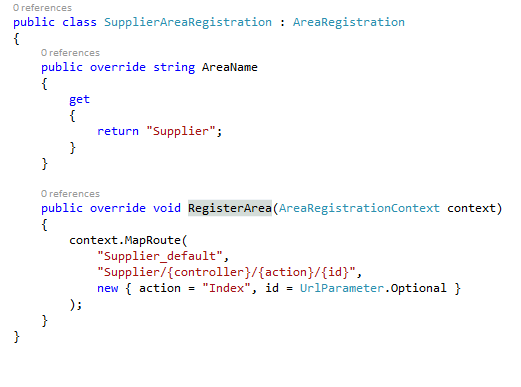
Defining a route is similar to defining a route for the whole project in RouteConfig.cs. However, it has one difference, which is very logical and makes sense, that the modular approach has even been applied to the routes as well. Meaning, as each area actually represents a module of your project, why shouldn't your URL represent the same? Therefore, each URL begins with the area name, indicating that the request is for a specific module only.
So the URL: http://localhost:1077/Suppliear/Home/Index is self-explanatory that it is a GET request for index action method of the Home controller of the Supplier module (Area).
However, if you do not like the modular implementation of your routes, you can change the route definition and remove the area name anytime. Though I will not recommend this.
If anything is registered, it must be called from somewhere. In ASP.NET MVC, whether it is your RegisterRoute method of the RouteConfig class or RegisterArea of the AreaRegistration class, it is called by the same event, which is none other than your Application_Start event in the global.asax file.