Session
Session generally means a time period for something. For example, when you log into Facebook, a new session starts, and you don't need to log in again to access other pages of your application. But after you log out, you need to log in again to access the pages. This is because the session ends. Keeping this in mind, we have a Session variable in ASP.NET where we generally store the user's information and destroy the session when the user logs out. Although we could store anything in a session, it is more suitable to store user-related information because this is what it was invented for.
- Session saves the data in the same way as any other dictionary object, that is, in key-value pairs where Key is a string and value is an object.
- As it stores the value as an object, type casting is necessary while retrieving the value.
- Also, it is recommended to do a null check before retrieving the value from the session to avoid a null exception.
- A session can be used to pass data from Controller to View or from Controller to Controller.
- The session is available throughout the application and does not get destroyed across multiple requests. In short, it can be used anywhere in the application until the session ends.
Let's understand this with an example:
Let's create two controllers and two Action Methods, one Action Method for each controller, and set the session value in the Action Method of the first controller and use it in the second controller's Action Method.
public class FirtsController: Controller
{
//
// GET: /Firts/
public ActionResult Index()
{
Session["Data"] = "Hello user welcome";
return View();
}
}
public class SecondController : Controller
{
//
// GET: /Second/
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Index";
}
<h2>First Controller's Index</h2>
@Session["Data"]
<a href="/Second/Index">Go to second controller</a>
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Index";
}
<h2>second contrller's Index</h2>
@Session["Data"]
Now, run the index of FirstController. You will get the following result:
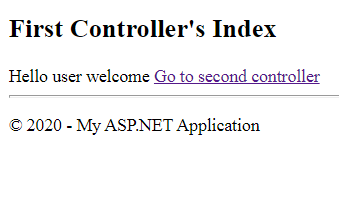
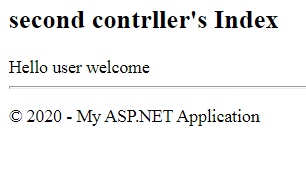
So, it can be concluded that the session persists the value across multiple requests and can be used across the whole project. As a session represents a user session, it is recommended to use a session only to store user-related data
