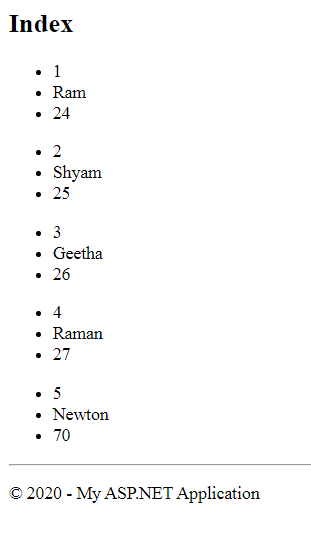A Model is simply a business entity in your application that may have some business rules defined. In layman's terms, a model is a class with fields, properties, and methods. Generally, a model only represents an Entity of your application, like Employee, Customer, etc, with properties or getters and setters.
The view that binds with any model is named a Strongly Typed View. We can bind any class as a model to look at and may access model properties from thereon. We can also use data associated with a model to render controls .
A strongly-typed view has the following advantages:
- Intellisense
- Compile time type checking
- Automatic scaffolding
In the previous article, we used ViewBag, ViewData, and TempData to pass information from the controller to the view. Remember, all of these do boxing-unboxing and are error-prone due to no IntelliSense support, as they accept a key as a string. So, it is always recommended to pass a model object from the controller to the view and make your view strongly typed.
Let's understand this with an example:
- Step 1. Create a class in your model folder with some properties like below.
public class Employee
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
public ActionResult Index()
{
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.Id = 1;
emp.Name = "Michael";
emp.Age = 22;
return View(emp);
}
@using MVCExample.Models
@model Employee
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Index";
}
<h2> Index</h2>
@Model.Id
@Model.Name
@Model.Age
Please note that first, I have imported the model's namespace and then used the Employee Type(class) as a model for the view.
To access the properties of the Employee object, I have used the Model property of the WebViewPage class, which is the parent class for every view in MVC.
Let's take an example with a list of Employee objects:
public ActionResult Index()
{
List<employee> employeeList = new List<employee> ()
{
new Employee(){Id=1,Name="Ram",Age=24},
new Employee(){Id=2,Name="Shyam",Age=25},
new Employee(){Id=3,Name="Geetha",Age=26},
new Employee(){Id=4,Name="Raman",Age=27},
new Employee(){Id=5,Name="Newton",Age=70},
};
return View(employeeList);
}
@using MVCExample.Models
@model IEnumerable<Employee>
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Index";
}
<h2> Index</h2>
@foreach(var item in Model){
<ul>
<li>@item.Id</li>
<li>@item.Name</li>
<li>@item.Age</li>
</ul>
}
Since I have passed a list of Employee from the controller to view, I had to use an IEnumerable of Employee objects as a model so that I could iterate through the list.