Set Operators are used to combine two result sets and produce a single result set. Many times, we need to combine two collections thoroughly. Sometimes, we want to combine collections but don't want to include the duplicate items; other times, we want to get all items that are in the first collection but are absent in the second collection. Due to all these requirements, we have the Set Operators in LINQ.
In LINQ, the Set Operators are used to return result sets based on the presence or absence of equivalent elements within the same or separate collections. LINQ provides us with the following Set operators, and each of the set operators has its own job:
- UNION
- INTERSECT
- DISTINCT
- EXCEPT
Set Operators can be used to combine elements of two collections completely, combine common elements between two collections, merge multiple collections, remove duplicate elements from the collection, and so on.
The following diagram shows more details related to the Set Operators in LINQ:
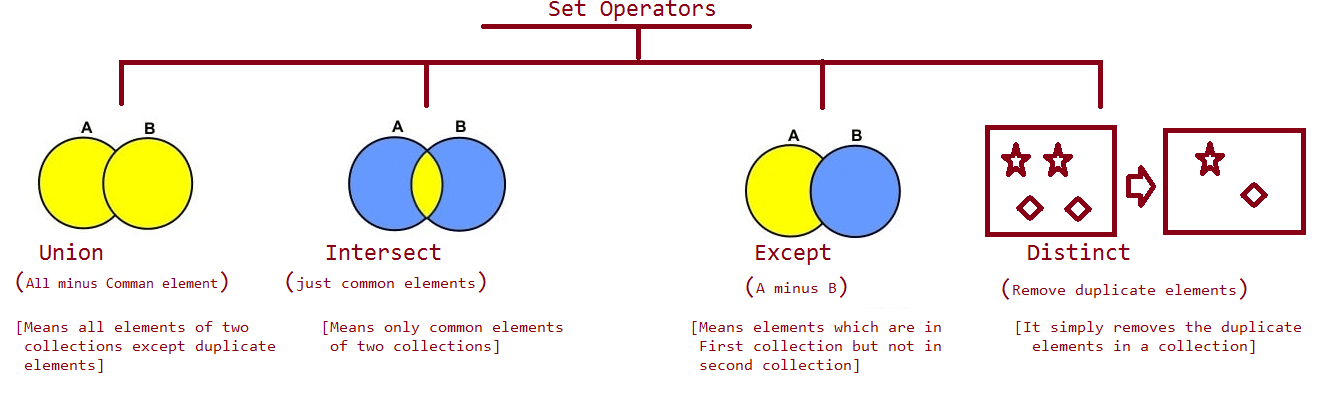
Union Operator
Union Operators are used to combine two collections and return a single collection after removing the duplicates. This means that the Union Operator will return a new collection containing all elements from the two collections except the common elements.
Example: Combine two collections and remove duplicates.
public static void Main()
{
List<string> strList1 = new List<string>() {"Ram","Shyam","Michael","Jhon","Peter" };
List<string> strList2 = new List<string>() { "Ram", "Sachin", "Arjun", "Vikash", "Jhon" };
var combination = strList1.Union(strList2);
foreach (var item in combination)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
Intersect Operator
Intersect Operators are used to return a new collection based on the common elements between the two collections.
Example: Return a collection containing common elements between two collections.
public static void Main()
{
List<string> strList1 = new List<string>() {"Ram","Shyam","Michael","Jhon","Peter" };
List<string> strList2 = new List<string>() { "Ram", "Sachin", "Arjun", "Vikash", "Jhon" };
var combination = strList1.Intersect(strList2);
foreach (var item in combination)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
Except Operator
Except Operators are used to return a new collection containing elements that are present in the first collection but are absent in the second collection.
Example: Return a collection containing such elements from the first collection that are not present in the second collection.
public static void Main()
{
List<string> strList1 = new List<string>() {"Ram","Shyam","Michael","Jhon","Peter" };
List<string> strList2 = new List<string>() { "Ram", "Sachin", "Arjun", "Vikash", "Jhon" };
var combination = strList1.Except(strList2);
foreach (var item in combination)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
Distinct Operator
Distinct Operators are used to return a new collection after removing the duplicates from the old collection.
Example: Return a collection after removing the duplicate items.
public static void Main()
{
List<string> strList1 = new List<string>
{"Ram","Shyam","Michael","Jhon","Peter","Ram","Jhon" };
var combination = strList1.Distinct();
foreach (var item in combination)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
In the upcoming chapters, we will learn more about each of these set operators in detail with examples.
