To understand the Element Operators, first analyze the following questions based on the collection shown below, and think about their solution:
List<int> numbers= new List<int>(){2,3,4,7,1,10};
- Find the first element in the collection
- Find the last element in the collection
- Find the 3rd element in the collection
- Find a single element divisible by 3. If more than one element is divisible by 3, return the default value
Notice that in all the questions mentioned above, we are trying to find a specific element in the collection, like the element at the first position, last position, a specific position, or a single element. For all these types of requirements, we have different element operators in LINQ like First(), Last(), ElementAt(), and Single() operators.
Now, look at the collection shown below. Notice, the collection is empty:
List<int> numbers= new List<int>();
If a collection is empty and you unknowingly try to find a specific element, you will get a null reference error. To solve this problem, LINQ provides the second version of the element operators like FirstOrDefault(), LastOrDefault(), SingleOrDefault(), etc.
In short, in LINQ, element operators are used to return a specific element from a collection. For example, with element operators, we can return the first element, last element, element at any specific position, or even a single element based on a specific condition, from the given collection.
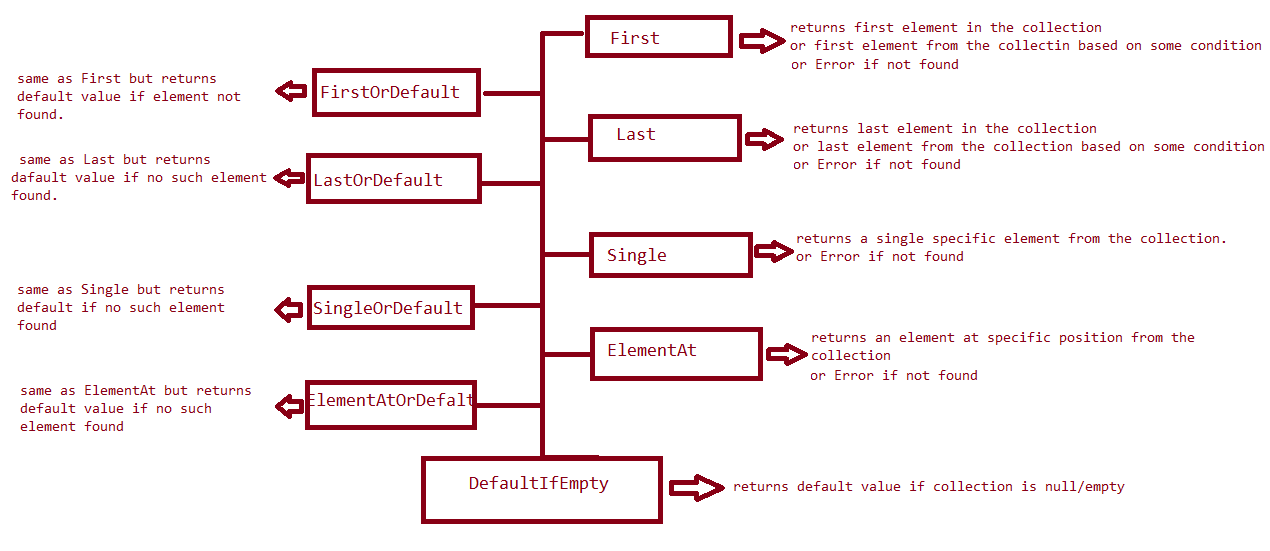
LINQ provides us following element operators:
- First
- FirstOrDefault
- Last
- LastOrDefault
- ElementAt
- ElementAtOrDefault
- Single
- SingleOrDefault
- DefaultIfEmpty
By using these element operators, we can get a specific element from the collection. The following diagram shows more detailed information related to element operators:
In the upcoming chapters, we will discuss all these element operators in detail with examples. We will be studying each of them with a demo so that we can get a clear understanding of these operators.
