In SQL Server, when we perform a LEFT join, all the records from the left table and only the matched records from the right table are included in the result set, and the non-matching records from the right table are excluded from the result set, as shown in the following diagram:
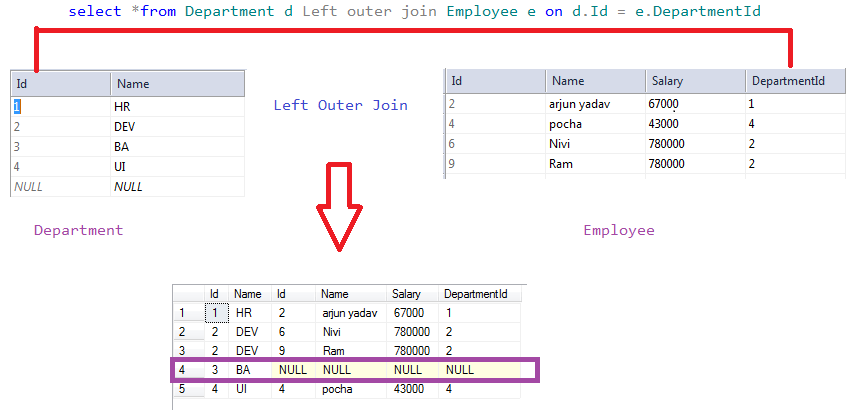
As you can see, the BA department has no employees, yet it is included in the result set.
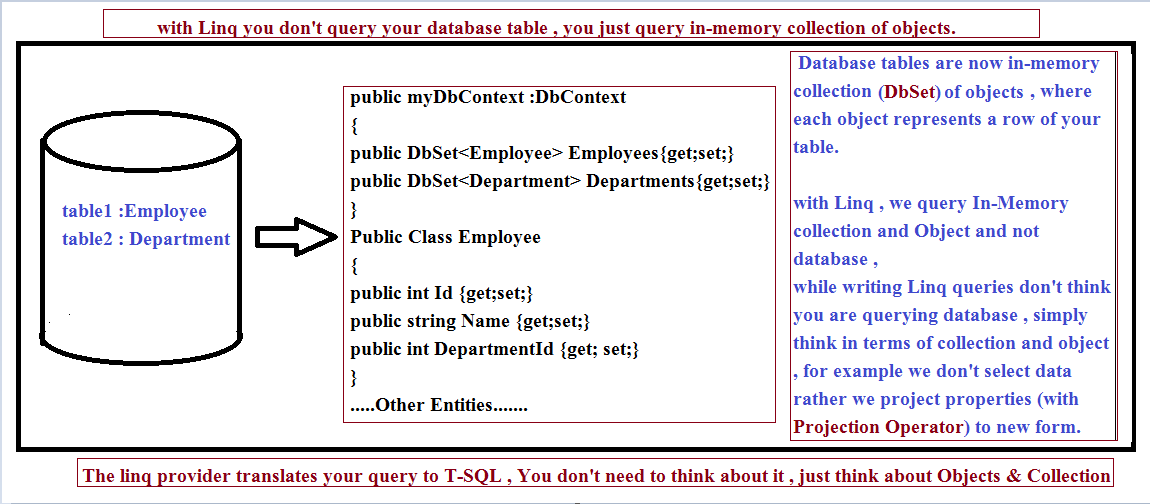
But with LINQ, we don't query a database table directly; rather, we query the collection of objects. The Entity Framework converts the tables into a collection of objects, and we simply query those collections (DbSets), and then the LINQ provider translates our query to corresponding T-SQL.
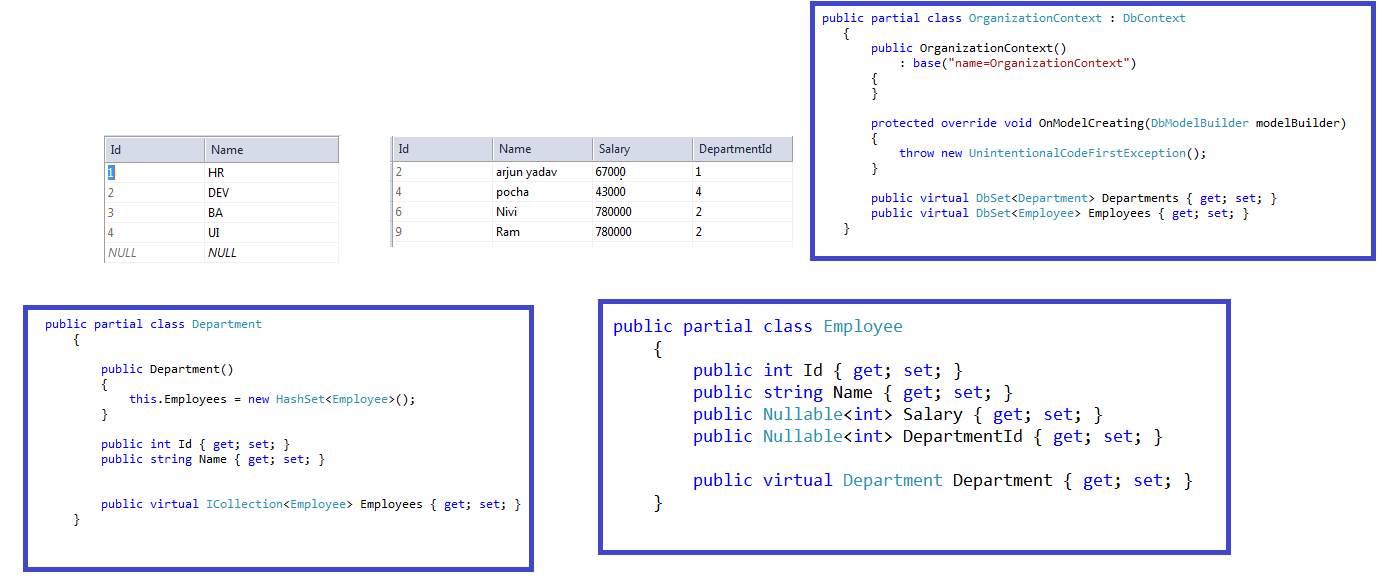
The Entity Framework will generate the following domain model based on the Employee and Department tables mentioned above:
In LINQ, we have no specific Join operator to perform a left outer join. We use the DefaultIfEmpty() method on the results of a group join to implement the Left Outer Join. If we have 2 collections, and we perform a Group Join and then apply the DefaultIfEmpty() method on the results, then all elements from the first collection and matching elements from the second collection are included in the result set, and the non-matching elements are excluded.
Left Join in Method Syntax
public static void Main()
{
OrganizationContext db = new OrganizationContext();
var result = db.Departments
.GroupJoin(db.Employees,
d => d.Id, e => e.DepartmentId, (dep, emps) => new { dep, emps }).SelectMany(g=> g.emps.DefaultIfEmpty(), (a, b) => new
{
Department = a.dep.Name,
EmployeeName = b == null ? "No Employee" : b.Name
});
foreach (var item in result)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} {1}", item.Department, item.EmployeeName);
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
The point is, to implement Left Outer Join, with extension method syntax we use the GroupJoin() method along with SelectMany() and DefaultIfEmpty() methods.
Output: Notice that, we also have BA department record in spite of it has no employees. So this is effectively a left outer join.

Left Outer Join in Query Syntax
We use the DefaultIfEmpty() method on the results of a group join to implement the Left Outer Join
Example: Rewrite the first example using SQL like syntax.
public static void Main()
{
OrganizationContext db = new OrganizationContext();
var result = from d in db.Departments
join e in db.Employees
on d.Id equals e.DepartmentId into eGroup
from e in eGroup.DefaultIfEmpty()
select new
{
Department = d.Name,
EmployeeName = e == null ? "No Employee" : e.Name
};
foreach (var item in result)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} {1}", item.Department, item.EmployeeName);
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.ReadLine();
}

