What is LINQ?
LINQ stands for Language Integrated Query. LINQ enables us to query a wide range of data sources with a similar coding style without having the need to know the syntax specific to the data source.
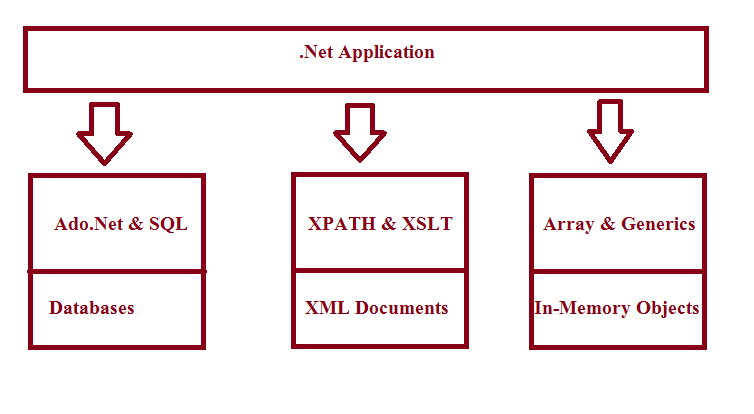
As you can see, in the above diagram, to query different data sources, we need to know different technologies. For example, to query databases, we need to know SQL and ADO.NET, to query XML documents, we need to know XPATH and XSLT, similarly, to query in-memory objects, we must have the knowledge of arrays and generics. Having the knowledge of these many technologies is not an easy task, but LINQ eliminates this issue, and now we can query any data source with LINQ operators easily in a uniform coding fashion.
LINQ was first introduced in .NET Framework 3.5 to query the data from different sources, such as collections, generics, XML documents, ADO.NET datasets, SQL, Web Services, etc., in C# and VB.NET using uniform query syntax.
LINQ contains a set of extension methods that allow us to query the different data sources in our application. We can't use any extension method until we import the namespace System.Linq, so please import the required namespace to use LINQ in your applications.
We can write LINQ queries in any .NET-supported programming language like C #, VB, etc.
LINQ Architecture
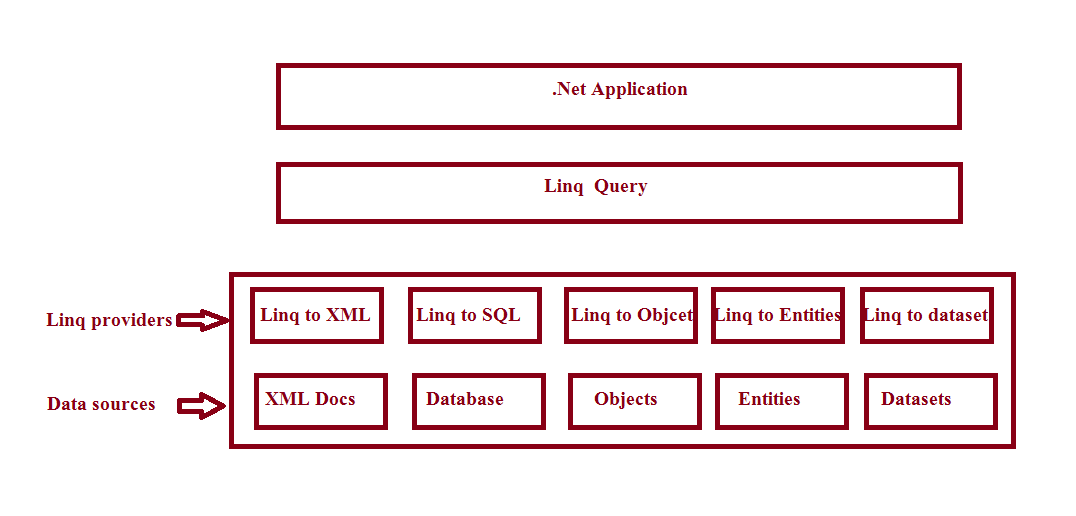
LINQ architecture is fairly simple. We write LINQ queries in any .NET-supported language like C# or VB.NET to query a data source. There resides a component between LINQ queries and the actual data source, which converts the LINQ query into a format that the underlying data source can understand. The component is called LINQ provider. There are several LINQ providers, as you can see in the above diagram. For example, LINQ to SQL provider converts a LINQ query to T-SQL that SQL Server database can understand.
Advantages of LINQ
- We don't need to learn different query languages for different data sources; LINQ works for all, and we can query all data sources with a similar coding style.
- In LINQ, we have to write less code in comparison to the traditional approach. This means LINQ minimizes the code, and the same thing is achieved with a few lines of code.
- LINQ provides compile-time error checking as well as intelligence support in Visual Studio, which helps developers like us to avoid run-time errors.
- LINQ provides a lot of built-in methods that we can use to perform different operations, such as filtering, ordering, grouping, etc., which makes our work easy.
- The query of LINQ can be reused.
Disadvantages of LINQ
LINQ is designed for simple queries. As your queries become more complex, LINQ starts to freak out. In such cases, the SQL queries that are generated at run time become significantly bulky and slow, so if you are working with a large database and you need to execute a complex query, it's better to write stored procedures and import them into your domain model (SP in database-first) instead of writing LINQ queries.
Different Ways of Writing LINQ Queries
LINQ queries are written with the help of LINQ extension methods or standard query operators, some of which are SELECT, FROM, WHERE, ORDER BY, JOIN, GROUP BY, etc. There are two ways or techniques to write LINQ queries using the standard query operators:
- Using LINQ syntax or SQL-like query expression as shown below:
var query= from e in context.Employees where e.Name.StartsWith("s") select e; - Using extension methods or lambda expressions as shown below:
var query= context.Employees.Where(x=>x.Name.StartsWith("s")).ToList();
Which method is better, the SQL-like query syntax method or the lambda expression method?
From a performance perspective, there is no difference between the two, and which one to use depends on personal preference. Please note that LINQ queries written using SQL-like query expressions are translated into their equivalent lambda expression before they are compiled.
The first approach is better for programmers who are more comfortable with SQL-style queries, whereas the second approach is better for programmers who are fine with lambda expressions, delegates, actions, and stuff like that.
But in many places, the extension method technique (lambda expression) is more powerful than LINQ syntaxes (SQL-like query expression). There are queries that you cannot write with SQL-like syntax easily or can't write at all, so learn both ways, but prefer to use extension methods.
