Sometimes, we may need to check whether all, some, or at least one element in the collection satisfies a given condition, and then we proceed further. For example, if you have to check whether any employee with a salary less than 25K exists or not, then, with plain C#, you will have to iterate over the Employees collection and check each employee's salary against the given condition. For such requirements, we have quantifiers in LINQ, which help in deciding whether some, all, or any element in the collection qualifies for a given condition or not.
All these methods return a Boolean value, i.e., True or False, depending on whether some or all of the elements in a collection satisfy a given condition.
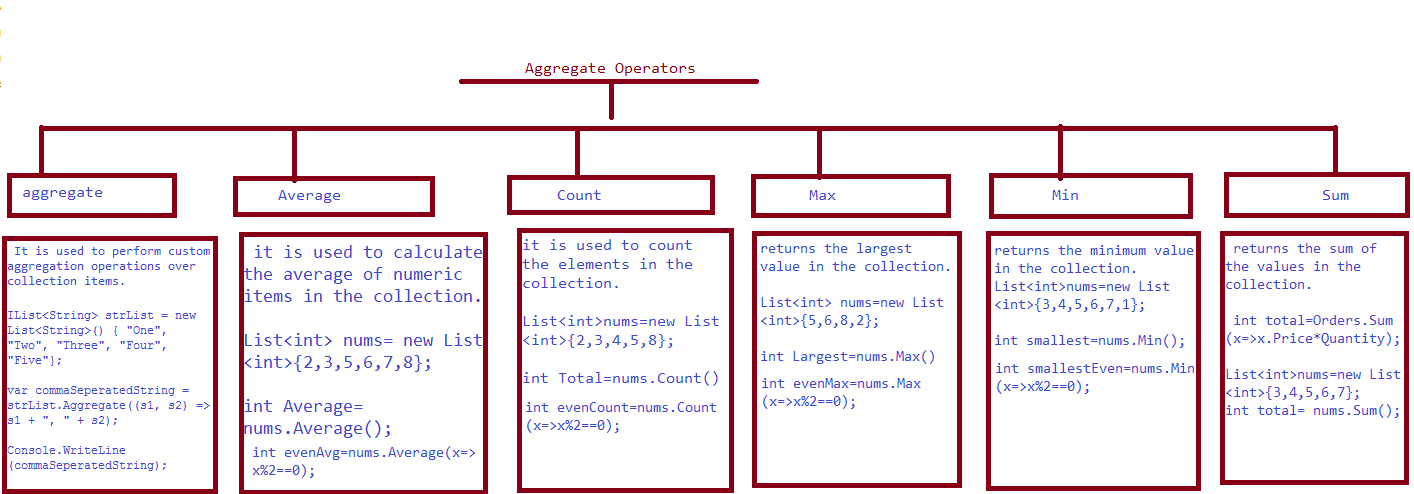
There are three quantifiers in LINQ:
- All
- Any
- Contains
The following diagram shows more detailed information related to quantifier operators:
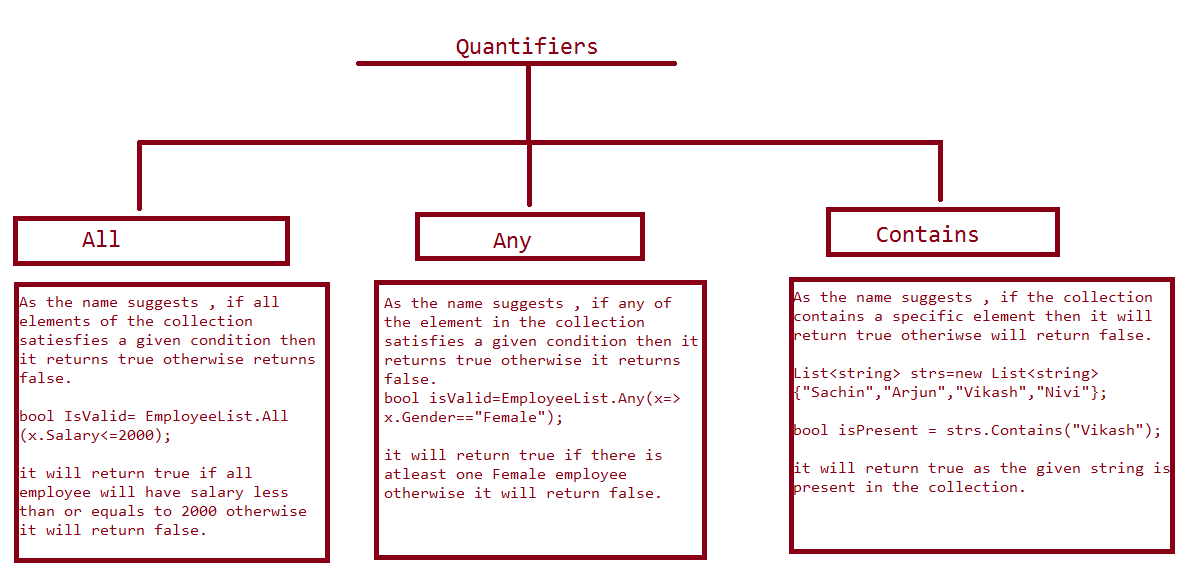
All
It is used to check whether all elements in the collection satisfy a given condition or not. If all the elements in the collection satisfy the condition, then it returns true; otherwise, it returns false. This means that even if one of the elements fails to qualify the condition, the All() operator will return false.
Example: Check all numbers in the list are even or not.
var numbers = new List<int>(){ 28, 35, 68, 72, 98 };
bool isAllEven = numbers.All(x => x % 2 == 0);
Console.WriteLine(isAllEven);
Any
It is used to check whether at least one element in the collection satisfies a given condition or not. If none of the elements in the collection qualify the condition, it returns false; otherwise, it returns true.
Example: Check whether an even number exists in the collection or not.
var numbers = new List<int>(){ 25, 35, 65, 75, 95 };
bool isAllEven = numbers.Any(x => x % 2 == 0);
Console.WriteLine(isAllEven);
Contains
It is used to check whether a specific element is present in the collection or not. If the specific element is present in the collection, the Contains() operator will return true; otherwise, it will return false.
Example: Whether "95" is present in the given list of integers or not.
var numbers = new List<int>(){ 25, 35, 65, 75, 95 };
bool isAllEven = numbers.Contains(95);
Console.WriteLine(isAllEven);
In the upcoming chapters, we will discuss all these LINQ quantifiers in detail with examples.