Before moving to the actual topic of how to call a stored procedure, let's first discuss what a stored procedure actually is.
What is an Stored Procedure?
A stored procedure is nothing but a group of T-SQL statements, which can contain 2 to 1000s of SQL statements. If an application uses the same query multiple times, we create a stored procedure for it, and call it by its name in the application
Advantages of Stored Procedures
There are several advantages of using the Stored Procedures over adhoc queries (inline SQL):
- If you write Inline SQL queries, maintaining them becomes a challenge. Also, you can't reuse them, but a Stored Procedure is created once and can be called several times whenever we need to execute some SQL queries. Thus, it enhances the reusability. At the same time, it decreases the maintenance load. Now, if we need to change something, we could just change the procedure, so we need to change it in one place.
- We also get security with a stored procedure. A database user can be granted access to an SP and could be prevented from executing direct "select" statements against a table.
- Inline SQL queries are built by concatenating user inputs, which opens the doors for SQL injection attacks, but the stored procedures prevent SQL injection attacks.
- A stored procedure is faster than inline queries because SQL Server retains the execution plan for SP. The stored procedures are compiled, and their execution plan is cached and used again when the same SP is executed.
- With the stored procedures, we only need to pass the stored procedure name from the application to the SQL Server, which reduces the network traffic.
Due to all these advantages, you may be asked to create SP and call them from your application.
Stored procedures are mainly of three types:
- SP without parameters.
- SP with input parameters.
- SP with output parameters.
Let's understand each of them one by one. To understand SP, we will need a database table, so let's create one:
- Step 1. Open the SQL Server Management Studio and run the following script. It will create a database with the name Test and two tables, Employee and Department, and populate them with some test data.
Create database Test
go
use Test
go
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Department] (
[Id] INT IDENTITY (1, 1) NOT NULL,
[Name] VARCHAR (50) NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Department] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED ([Id] ASC)
);
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Employee] (
[Id] INT IDENTITY (1, 1) NOT NULL,
[Name] VARCHAR (50) NULL,
[Salary] INT NULL,
[DepartmentId] INT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Employee] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED ([Id] ASC),
CONSTRAINT [FK_Employee_Department] FOREIGN KEY ([DepartmentId]) REFERENCES [dbo].[Department] ([Id])
);
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].[Department] ON
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Department] ([Id], [Name]) VALUES (1, N'HR')
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Department] ([Id], [Name]) VALUES (2, N'Development')
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Department] ([Id], [Name]) VALUES (3, N'Database')
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Department] ([Id], [Name]) VALUES (4, N'Business')
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].[Department] OFF
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].[Employee] ON
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Employee] ([Id], [Name], [Salary], [DepartmentId]) VALUES (1, N'sachin', 100000, 1)
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Employee] ([Id], [Name], [Salary], [DepartmentId]) VALUES (2, N'arjun', 23000, 1)
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Employee] ([Id], [Name], [Salary], [DepartmentId]) VALUES (3, N'vikash', 30000, 2)
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Employee] ([Id], [Name], [Salary], [DepartmentId]) VALUES (4, N'pocha', 43000, 3)
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Employee] ([Id], [Name], [Salary], [DepartmentId]) VALUES (5, N'Nivedita', 24000, 4)
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].[Employee] OFF
<connectionStrings>
<add name="CS" connectionString="Data Source=SACHIN-PC\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=Test;Integrated Security=True"/>
</connectionStrings>
SP without parameters (display all employees with their department in a GridView.)
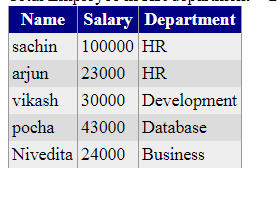
- Step1. Create the procedure.
create procedure spGetEmployees
as
begin
select emp.Name,emp.Salary,dep.Name from Employee emp
join Department dep
on emp.DepartmentId=dep.Id
end
private void BindGrid()
{
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(cs))
{
//Create the SqlCommand object
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("spGetEmployees",con);
//Specify that the SqlCommand is a stored procedure
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
//Open the connection, execute the query, and bind the grid
con.Open();
GridView1.DataSource = cmd.ExecuteReader();
GridView1.DataBind();
}
}
Please note that to call a stored procedure, we simply specify the name of the SP in the constructor of the SqlCommand object, and then specify the command type as usual. To execute the command, we use the ExecuteReader() method.
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!IsPostBack)
{
BindGrid();
}
}
SP with input parameters (Add employee details into the database.)
- Step 1. Create the stored procedure.
create procedure spAddEmployee
@Name varchar(50),
@Salary int,
@DepId int
as
begin
insert into Employee values (@Name,@Salary,@DepId)
end
<table border="1" style="background: brown; color: White">
<tr>
<td>Name</td>
<td><asp:TextBox ID="txtName" runat="server"></asp:TextBox></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Salary</td>
<td><asp:TextBox ID="txtSalary" runat="server"></asp:TextBox></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Department</td>
<td>
<asp:DropDownList ID="ddlDepartment" runat="server" DataTextField="Name" DataValueField="Id"></asp:DropDownList>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">
<asp:Button ID="Button1" runat="server" Text="Insert" OnClick="Button1_Click"/>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!IsPostBack)
{
BindGrid();
BindDepartment();
}
}
private void BindDepartment()
{
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(cs))
{
SqlDataAdapter da = new SqlDataAdapter("select * from Department", con);
da.Fill(ds);
}
ListItem li = new ListItem() { Text = "Please Select", Value = "-1" };
ddlDepartment.Items.Insert(0, li);
ddlDepartment.DataSource = ds;
ddlDepartment.DataBind();
}
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(cs))
{
//Create the SqlCommand object
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("spAddEmployee", con);
//Specify that the SqlCommand is a stored procedure
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
//Add the input parameters to the command object
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Name",txtName.Text);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Salary", txtSalary.Text);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@DepId", ddlDepartment.SelectedItem.Value);
//Open the connection and execute the query
con.Open();
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
BindGrid();
}
}
Please notethat here, we are specifying SP name in the constructor of SqlCommand object, specifying the command type as a stored procedure, and then providing necessary input parameters using AddWithValue() method.
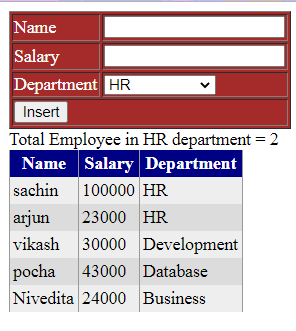
SP with output parameters (display the total count of employees in the HR department in a label)

- Step 1. Create SP
To create an SP with an output parameter, we use the keywords OUT or OUTPUT. @empCount is an OUTPUT parameter. Notice, it is specified with the OUT keyword.
create procedure spGetHrEmployeeCount
@empCount int out
as
begin
select @empCount =Count(*) from Employee
where DepartmentId = (Select Id from Department where Name='HR')
end
private void GetHrCount()
{
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(cs))
{
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("spGetHrEmployeeCount", con);
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
//Add the output parameter to the command object
SqlParameter outPutParameter = new SqlParameter();
outPutParameter.ParameterName = "@EmployeeId";
outPutParameter.SqlDbType = System.Data.SqlDbType.Int;
outPutParameter.Direction = System.Data.ParameterDirection.Output;
cmd.Parameters.Add(outPutParameter);
//Open the connection and execute the query
con.Open();
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
//Retrieve the value of the output parameter and set the label Text
string HrCount = outPutParameter.Value.ToString();
lblMessage.Text = "Total Employee in HR department = " + HrCount;
}
The complete source code looks like below:
Code Behind (aspx.cs)
public partial class StoreProcedureExample : System.Web.UI.Page
{
string cs = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["CS"].ConnectionString;
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!IsPostBack)
{
BindGrid();
BindDepartment();
GetHrCount();
}
}
private void BindGrid()
{
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(cs))
{
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("spGetEmployees",con);
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
con.Open();
GridView1.DataSource = cmd.ExecuteReader();
GridView1.DataBind();
}
}
private void BindDepartment()
{
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(cs))
{
SqlDataAdapter da = new SqlDataAdapter("select * from Department", con);
da.Fill(ds);
}
ListItem li = new ListItem() { Text = "Please Select", Value = "-1" };
ddlDepartment.Items.Insert(0, li);
ddlDepartment.DataSource = ds;
ddlDepartment.DataBind();
}
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(cs))
{
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("spAddEmployee", con);
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Name",txtName.Text);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Salary", txtSalary.Text);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@DepId", ddlDepartment.SelectedItem.Value);
con.Open();
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
BindGrid();
}
}
private void GetHrCount()
{
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(cs))
{
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("spGetHrEmployeeCount", con);
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
//Add the output parameter to the command object
SqlParameter outPutParameter = new SqlParameter();
outPutParameter.ParameterName = "@empCount";
outPutParameter.SqlDbType = System.Data.SqlDbType.Int;
outPutParameter.Direction = System.Data.ParameterDirection.Output;
cmd.Parameters.Add(outPutParameter);
//Open the connection and execute the query
con.Open();
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
//Retrieve the value of the output parameter
string HrCount = outPutParameter.Value.ToString();
lblMessage.Text = "Total Employee in HR department = " + HrCount;
}
}
}
The HTML (aspx page)
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
<table border="1" style="background: brown; color: White">
<tr>
<td>Name</td>
<td> <asp:TextBox ID="txtName" runat="server"></asp:TextBox></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Salary</td>
<td><asp:TextBox ID="txtSalary" runat="server"></asp:TextBox></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Department</td>
<td>
<asp:DropDownList ID="ddlDepartment" runat="server" DataTextField="Name" DataValueField="Id"></asp:DropDownList>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">
<asp:Button ID="Button1" runat="server" Text="Insert" OnClick="Button1_Click"/>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<asp:Label Text="text" runat="server" ID="lblMessage" />
<asp:GridView ID="GridView1" runat="server" BackColor="White" BorderColor="#999999" BorderStyle="None" BorderWidth="1px" CellPadding="3" GridLines="Vertical">
<AlternatingRowStyle BackColor="#DCDCDC" />
<FooterStyle BackColor="#CCCCCC" ForeColor="Black" />
<HeaderStyle BackColor="#000084" Font-Bold="True" ForeColor="White" />
<PagerStyle BackColor="#999999" ForeColor="Black" HorizontalAlign="Center" />
<RowStyle BackColor="#EEEEEE" ForeColor="Black" />
<SelectedRowStyle BackColor="#008A8C" Font-Bold="True" ForeColor="White" />
<SortedAscendingCellStyle BackColor="#F1F1F1" />
<SortedAscendingHeaderStyle BackColor="#0000A9" />
<SortedDescendingCellStyle BackColor="#CAC9C9" />
<SortedDescendingHeaderStyle BackColor="#000065" />
</asp:GridView>
</div>
</form>